Forklift Trucks
Safe Handling of Propane (LPG) Fuel
DO’s
POSITION the tank so liquid does not come in contact with the relief valve.
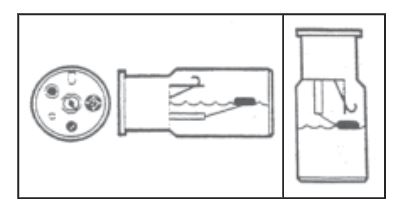
CHECK to see locking pin engages into cylinder.
STORE cylinder outside, in an upright position in an area where they can be secured and protected from being struck. Remember valve should be closed tightly.
PUT cylinder down gently. Do not drop.
ALWAYS protect valve
AVOID contact with propane. Rapid vapourization can cause frostbite.
WEAR protective gloves while making or breaking connections.
USE only components approved by the Canadian Gas Association (CGA), Canadian Standards Association (CSA), Canadian Transport Comission (CTC), Underwriters Laboratories Inc.(UL) or Underwriters Laboratories Canada (ULC).
ENSURE that repairs to the caburetor or fuel supply system are done by qualified (LPG) service person.
EXCHANGE removable cylinders outdoors or in well ventilated areas, away from sources of ignition.
CLOSE valve before breaking connections.
DO NOT’s
DO NOT USE metal tools when changing cylinders.
DO NOT LET cylinder get to hot.
DO NOT MOUNT more than two (LPG) cylinders on any forklift truck.
CHANGING FUEL TANKS
Procedure for changing propane (LPG) cylinders:
- Wear eye protection and leather gloves
- Close valve on cylinder.
- Run engine until it stops. This ensures that the supply hose is empty.
- Shut off engine.
- Open connecting nut (inspect valves for leaking).
Do not use metal tools. - Disconnect hose.
- Disconnect holding straps.
- Remove empty cylinder.
- Replace with full cylinder in proper position.
- Connect holding straps.
- Tighten connecting nut (wiggle hose).
- Open valve on cylinder slowly. Check for leaks.
Use soap and water solution. Smell – Listen – Look. - If no leaks are found, start motor and resume operation. If leaks are present repeat installation procedure. If leaks continue, have unit repaired by authorized (LPG) service personnel.
Forklift Trucks
Maintenance
DO’s
PERMIT only qualified persons to service and maintain equipment.
DISCONNECTall batteries and propane before any work is done.
KEEP work area clean, and well lit.
CLEAN spilled oil or hydraulic fluid immediately.
WEAR proper personal protective equipment. Wear goggles when grinding. Wear face shields, aprons and rubber boots when working around battery charging equipment. Wear gloves when changing (LPG) fuel tanks.
BLOCK forklift securely when removing wheels.
ENSURE all tools and parts are removed before starting engine.
SUPPORT forklift hood in upright position or remove when required to do work.
HANDLE batteries with care.
AVOID contact of battery terminals with hoisting chains, tools or metal objects.
COVER battery top with some insulating material.
CHECK bolts that hold counterweight to the frame and replace worn or missing bolts.
INSPECT forks for distorted, twisted, worn or bent sections.
CHECK operator’s daily checklist and have repairs made as required.
DO NOT’s
DO NOT LEAVE parts, creepers, cans, tools or other obstacles around.
DO NOT LIFT beyond your capacity. Use hoist or leverage tools to lift or move heavy parts or equipment.
DO NOT SMOKE, weld or light a match around refueling or battery charging areas.
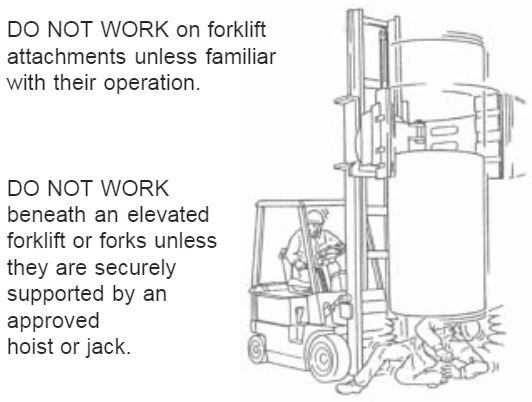
DO NOT RUN (LPG), Gas or Diesel forklift in unventilated areas.
Forklift Trucks
Fork Safety
FORK INSPECTION SCHEDULE
Under normal operating conditions, forks should be inspected daily and every six months.
DAILY: A visual inspection of forks (by operator) is done on the pre-start up check, with special attention to cracks and deformation.
SIX MONTHS:A thorough inspection of forks is done looking for cracks wear and deformation. This inspection may be required more often depending on the use of the equipment.
CHECKLIST
DO’s
CHECK fork blades for wear. Forks are constantly to abrasion, by concrete floors, steel shelving, etc. This abrasion can reduce the thickness of a fork until it is not capable of lifting to design capacity.
CHECK for distortion. Forks can be bent out of shape. Depending on the degree of distortion some forks can be straightened. Contact your forklift supplier regarding for repairs.
CHECK for cracks in heel and hanger. Cracks may appear in forks where (a) attachments are welded (b) in the inside radius of the bend area, Cracks can be discovered by periodic inspection using the dye penetrant or magnetic particle methods of testing. Some of these blemishes may be ground out and polished by approved grinding methods, depending on the depth of the crack. Contact your forklift supplier.
REPLACE with quality forks. When you order forks, make sure your getting high quality forks that will perform you lifting jobs in a safe and dependable manner. Insist on forks that are forged.
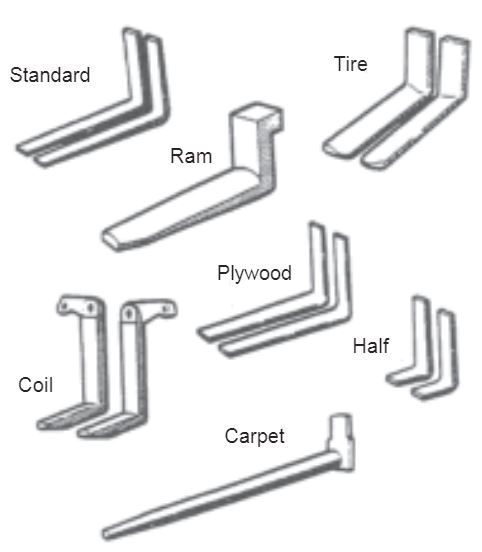
USE the proper forks. Custom designated forks are needed for:
-unusual lifting conditions
-spark free areas
Contact your forklift supplier for assistance.
DO NOT’s
DO NOT OVERLOAD. Operators should be aware of the capacity of the forklift, as well as the capacity of the forks. Overloading may bend and weaken forks.
FORK REPAIRS AND MODIFICATIONS should be carried out by your forklift supplier or the fork manufacturer.
Forklift Trucks
Ergonomics
VEHICLE CAPABILITY
Is the forklift capable of handling the required lift and load size?
Is the forklift designed to operate in the assigned area of operation?
Is the forklift stable in all lift and operating positions?
Is the load capacity clearly marked on the forklift?
Will the floors support the weight of the loaded forklift?
Can the forklift make the necessary turns within its area of operation?
Is there sufficient width and overhead clearance for the forklift to clear structures and walkways?
Does the forklift have the required height and or reach to place the load?
OPERATOR VISIBILITY
Does the operator have a good view:
-upward
-of the ground(i.e. a squatting person at 5 metres)(br)-in directions of work without assuming a twisted position.
LIGHTING
Is the lighting sufficient in all directions of travel and work?
Is the engine compartment lighting adequate for ease and safety of inspection?
Is the forklift lighting adequate (signal, brake and parking lights: headlights, revolving roof light?) As well as acceptable lighting to and from forklift cab.
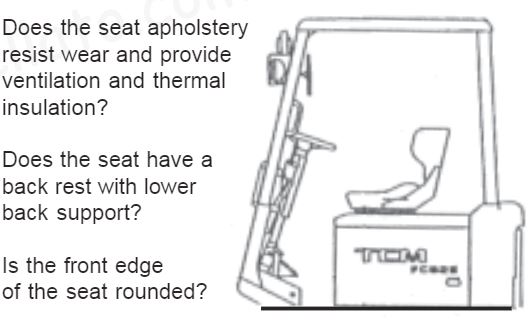
SEATING
Is the seat provided with a shock-absorbing system?
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Make sure the forklift is equipped with these safety devices:
-Back-up alarm
-Rear view mirror
-High visibility colour. Back of forklift striped with reflective tape.
-Fire extinguisher.
-Adequate and readily accessible emergency shutdown.(Dead man seat).
-Roll over protection and seat belts.
-Air, hydraulic and fuel lines protected from heat and abrasive objects.
-Guarding or shielding of exhaust stack, service platform e.t.c
-Special tires (comfort,traction).